FAQs
What is end-to-end encryption?
End-to-end encryption is a term we keep hearing more and more of. What does it mean? And why is it so important now?

Just a heads up, if you buy something through our links, we may get a small share of the sale. It’s one of the ways we keep the lights on here. Click here for more.
Data breaches are as common as morning coffee, so securing our online conversations is more crucial than ever. That’s where end-to-end encryption comes in, a term you’ve likely heard but might not fully understand.
Put simply, end-to-end (E2EE) is the ironclad lockbox that keeps prying eyes away from your private information, specifically in things like messages, emails, and more.
It’s a security measure that ensures only the sender and intended recipient can access the encrypted data, preventing unauthorized access from third parties or prying eyes
I’ll explain the complexities of end-to-end encryption and highlight its crucial role in ensuring digital security.
Whether you’re sending a text, making a call, or sharing files, knowing how this technology works is key to protecting your digital footprint. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mystery of end-to-end encryption together.
What is end-to-end encryption?
Short answer: End-to-end encryption is a secret message that only the person you’re sending it to can understand. It keeps your information private and safe from anyone else who might try to see it.
In E2EE, the data is encrypted on the sender’s system, and only the recipient is able to decrypt and read it.
Whoever intercepts the data during transfer sees only scrambled, unintelligible text. This is paramount for preserving the privacy of digital communications.
How it works
E2EE operates on a process where only the communicating users hold the keys to unlock and read the messages. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the steps involved:
- The sender uses the recipient’s public key to encrypt the message.
- The encrypted message travels across the internet, safe from prying eyes.
- The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the message upon arrival.
This ensures that the message remains secure throughout its journey, and even if the message is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the corresponding private key.
Advantages of end-to-end encryption
E2EE offers numerous benefits, which I find significant in today’s digital landscape:
- Confidentiality: Only the sender and intended recipient can view the message contents.
- Data integrity: E2EE ensures that the content has not been tampered with, keeping the original message intact.
- Protection against eavesdropping: It thwarts any unauthorized parties who try to listen in on your conversations.
- Trust: Users can be confident that their communications are private and secured from vulnerabilities.
These advantages help users feel more secure when sharing sensitive information over the internet.
Common applications of end-to-end encryption
End-to-end encryption is super important because it’s used in loads of digital services that really care about keeping your stuff private and secure.
Messaging apps

E2EE has become synonymous with privacy. Apps like WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram are flag bearers, encrypting messages in a way that only the sender and receiver can read them.
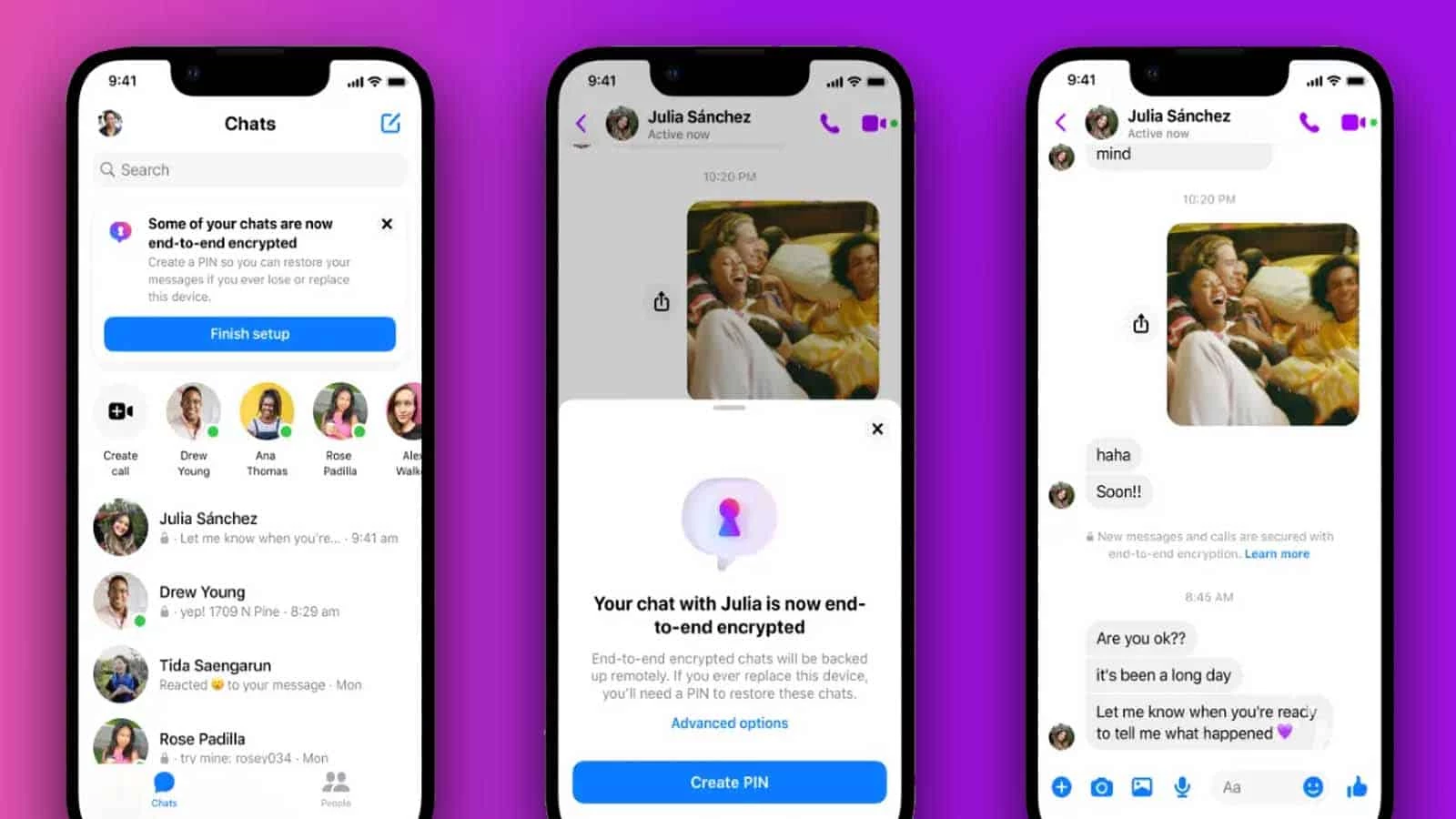
And now Meta, Facebook’s parent company is jumping on the end-to-end encryption train and now locking Messenger chats with E2EE by default.
The moment a message leaves my device, it’s wrapped in a secure blanket of encryption, traveling through servers as an indecipherable code until it safely arrives at the intended recipient’s device, where it can finally be deciphered.
This ensures that:
- My conversations remain confidential
- There’s a reduced risk of message interception
- Only the recipient and I have access to the content
Every text, photo, or call made through these apps is shielded, providing a strong layer of security against potential breaches.
Email services

Some email services, like ProtonMail and Tutanota, use end-to-end encryption (E2EE) to keep your emails safe.
With E2EE, your email is encrypted on your device before it’s sent, so even if someone intercepts it, they won’t be able to read it unless they’re the intended recipient.
Some key benefits of end-to-end encrypted email services include:
- Protection from unauthorized access and cyber threats
- Ensuring that sensitive information stays hidden
- Peace of mind knowing that private conversations aren’t at risk
It’s vital to recognize that not all email providers offer E2EE by default. It’s my responsibility to choose a service that aligns with my security needs.
Cloud storage

The rise of cloud computing has resulted in more people and businesses using cloud storage services. Services such as iCloud, Google Drive, and Dropbox are incorporating end-to-end encryption to protect the stored files.
With E2EE, users’ documents and photos are encrypted on their own devices and stay encrypted until they are accessed again.
It’s essential for me to note that the level and implementation of E2EE can vary across cloud services. Some may require additional steps or configurations to fully secure my data with end-to-end encryption.
End-to-end encryption vs. regular encryption
Understanding the distinction between end-to-end encryption and regular encryption is crucial for recognizing the layer of security each one provides.
While they both aim to protect data, their approaches and strengths differ significantly.
Differences
Regular encryption secures data in transit but may leave it accessible at endpoints where service providers could access it. Key differences include:
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is more secure than regular encryption because only the sender and receiver can read the messages, and the decryption keys are kept exclusively with the end users.
Regular encryption is more vulnerable to data breaches since decryption keys might be accessed by third parties if they are stored on servers.

Whereas E2EE remains secure even if attackers gain access to servers since they cannot obtain the necessary keys to decrypt the messages.
Understanding these differences is important for informed decisions on data security and privacy.
However, it’s also important to understand that no system is infallible. User’s endpoints, like smartphones or computers, must be secure as well, since E2EE only protects data in transmission and not on the device itself.
High-profile cyber attacks have exploited endpoint vulnerabilities, emphasizing the need for comprehensive security measures beyond just secure transmission.
End to End Encryption – Wrapping it all up

End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is like a secret code that keeps your online chats private. It’s an important step to protect your messages from being seen by anyone else.
With E2EE, it becomes difficult for curious people and snoops to access your conversations. In a world where data leaks are common, E2EE is a reliable way to keep your private information secure on the internet.
And let’s face it, with all this chat about data leaks popping up left and right, having E2EE feels less like a luxury and more like a trusty guardian for keeping private things private in our wild and wacky internet world.
Have any thoughts on this? Drop us a line below in the comments, or carry the discussion to our Twitter or Facebook.
Editors’ Recommendations:
- Meta locks up Messenger chats with default end-to-end encryption
- How to update your iPhone to get end-to-end encryption
- How to enable end-to-end encryption on Messenger
- Facebook is finally testing default encryption in Messenger