Tech
2.4GHz vs 5GHz – what’s the difference?
With a bit of tinkering, you’ll have all your gadgets humming along on the perfect network in no time.

Just a heads up, if you buy something through our links, we may get a small share of the sale. It’s one of the ways we keep the lights on here. Click here for more.
Quick Answer: 2.4GHz and 5GHz are two different frequencies used by Wi-Fi routers to transmit data wirelessly. 5GHz provides faster speeds but has a shorter range, while 2.4GHz has a longer range but slower speeds.
2.4GHz vs. 5GHz: it’s a question that has puzzled many of us.
Most people have little to no idea about the difference between these two network frequencies, let alone which one is better for their needs.
To gain some insight into this topic, I asked five friends if they knew what 5GHz was and if they had ever connected to it. Their answers were not surprising.
Four out of five said they had no idea what it was, and the fifth one only had a vague idea that he could use it when the other network wasn’t working. Pretty sound logic; I can’t argue with that.
See? It’s pretty confusing. Many people don’t have a clear idea of what these terms mean or how they work. But the good news is that we’re here to help.
In this article, we’ll provide you with all the information you need to navigate the mysterious world of Wi-Fi networks. We’ll even speak to an expert network engineer who sheds some light on the topic.
Whether you need longer-range or faster Wi-Fi speeds, we’ll show you which frequency to choose for your devices, leaving you free to connect and surf in no time.
Ready to dive in?
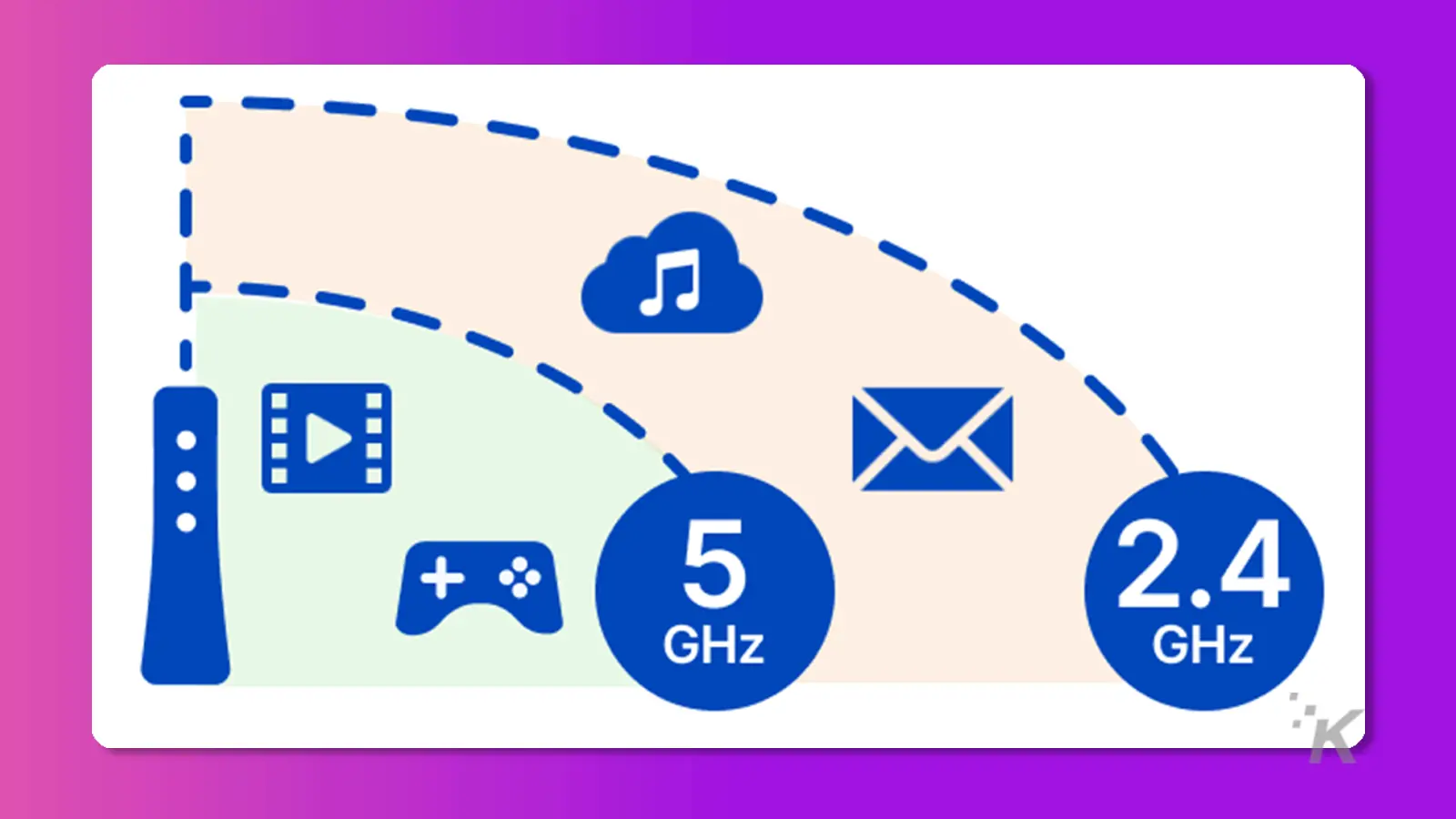
What’s the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Short Answer: One offers longer range, while the other offers faster speeds with a shorter range.
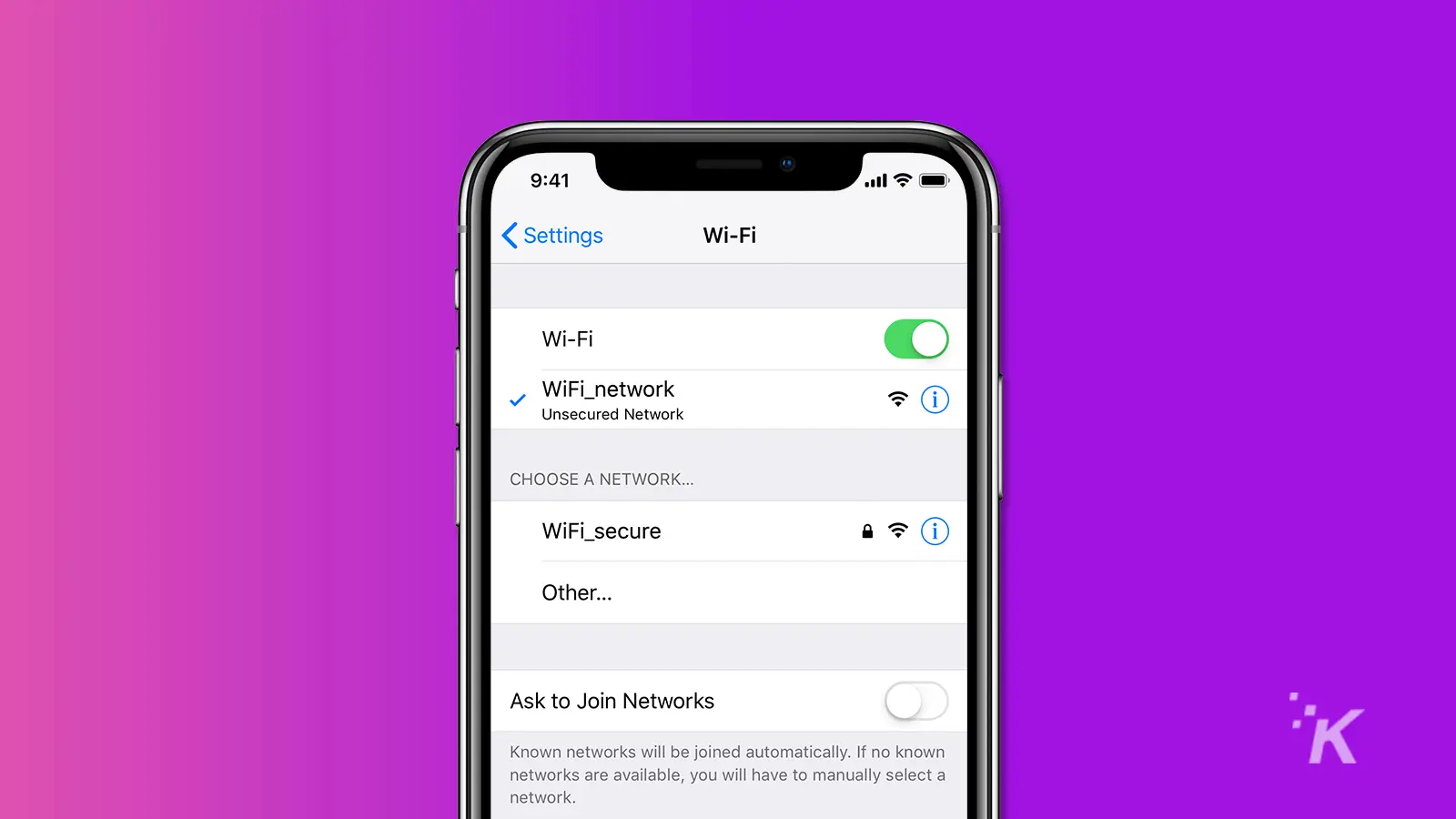
2.4GHz Wi-Fi networks have a longer range and can penetrate walls better, but the network tends to be slower and more congested.
A gigahertz (GHz) is a way to measure how fast a computer’s brain, called the processor, can think and do things. It tells us how many cycles, or tiny operations, the processor can complete in just one second.
Think of it like this: if you have two cars driving at different speeds, the one that goes faster will reach its destination quicker. Similarly, a CPU with a higher gigahertz rating can process information and perform tasks more quickly than one with a lower rating.
So when you see a CPU with a higher gigahertz value, it means that computer has more “brain power” and can handle tasks faster. It’s like having a super smart friend who can solve problems and get things done really quickly!
In simple terms, gigahertz is just a way to measure how fast your computer’s brain works. The higher the number, the faster your computer can think and get things done efficiently.
On the other hand, 5GHz Wi-Fi networks are faster and less congested but have a shorter range and struggle to penetrate walls.
Additionally, 5GHz networks are more congested in urban environments as most non-IoT devices now use this frequency
| Standard | Transmission Speed | RF Range |
|---|---|---|
| IEEE 802.11 | 1-2 Mbps | 2.4GHz |
| IEEE 802.11a | Up to 54Mbps | 5GHz |
| IEEE 802.11b | Up to 11Mbps | 2.4GHz |
| IEEE 802.11g | Up to 54Mbps | 2.4GHz |
| IEEE 802.11n | Up to 600Mbps | 2.4GHz/5GHz |
The expert’s take
Chris Hendrie, CEO and network engineer at BlackStar Group, provides his expert viewpoint:
“The main difference between the two frequency spaces: Do you need range or throughput? 2.4 will get you 2x or more the “distance” for your signal, but you’re capped at 400Mbps,” Hendrie explains to KnowTechie.
“5GHz will get you 1.3Gbps (or more, depending on implementation), but its range is significantly reduced, especially through walls.”
When is 5GHz Wi-Fi better than 2.4GHz?
This type of network is ideal for situations where you need faster speeds and lower latency, such as online gaming or streaming 4K video.
5GHz networks have a higher frequency, meaning they can transmit more data in a shorter time. They’re also less congested, as fewer devices use this frequency.
So, if you’re a heavy internet user who demands fast, reliable speeds, 5GHz is your best bet.
What devices should be on 2.4GHz and 5GHz?

Choosing which devices to put on 2.4GHz and which to put on 5GHz can be a bit tricky, but we’ve got some tips to help you out.
What devices use 2.4GHz?
Let’s start with 2.4GHz. This type of network is perfect for smart home devices that don’t require a lot of bandwidth, such as smart plugs and smart lights.
It’s also a good choice for devices that don’t move around much, such as desktop computers or printers.
Basically, if you have a device that doesn’t need to move around and doesn’t require a lot of data, 2.4GHz is the way to go.
What devices use 5GHz
Now, let’s talk about 5GHz. This type of network is ideal for devices that require faster speeds and lower latency, such as laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles.
It’s also a good choice for streaming devices, such as smart TVs or streaming sticks, as they require a lot of data and benefit from the faster speeds of 5GHz.
Of course, there are exceptions to these rules, and it ultimately depends on your specific situation. For example, if you have a laptop you use for work and require a stable, high-speed connection, you should put it on 5GHz even if it doesn’t necessarily need it.
On the flip side, if you have a smart home device that you barely use, like a sprinkler system or a garage door opener, you can probably get away with putting it on 2.4GHz, even if it requires a little bit of data.
The difference between 5GHz and 2.4GHz is all about speed and range

At the end of the day, it’s all about finding the sweet spot that works best for you and your devices.
I prefer to keep my MacBook Pro connected to 5GHz, while my iPhone 14 Pro Max stays on the 2.4GHZ. The only device I still struggle with is my security cams; it’s a cat-and-mouse game I’ve yet to figure out.
Wrapping things up here: experiment with different configurations, see what feels right, and go from there. With a little bit of tinkering, you’ll have all your gadgets humming along on the perfect network in no time.
Have any thoughts on this? Drop us a line below in the comments, or carry the discussion over to our Twitter or Facebook.
Editors’ Recommendations:
- Can’t remember Xfinity router password? Here’s what to do
- Xfinity remote not working? Here’s how to fix it
- How do Apple AirTags work?
- How many mesh routers do you need for your home?
Just a heads up, if you buy something through our links, we may get a small share of the sale. It’s one of the ways we keep the lights on here. Click here for more.